-
What’s Hot in Sustainable Investing
Introduction
Sustainable investing has become a major focus for investors worldwide, driven by growing awareness of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues. This approach not only aims to generate financial returns but also to create positive impacts on society and the environment. Let’s explore the latest trends, market analysis statistics, and examples of sustainable investments, along with the impacts from the Trump government and EU responses.
Current Trends in Sustainable Investing
- Climate-Transition Investing: Investors are increasingly focusing on companies that are actively transitioning to low-carbon operations. This includes investments in renewable energy, energy efficiency, and carbon capture technologies. Companies that are leading the way in reducing their carbon footprints are attracting significant investor interest.
- Sustainable Bonds: The issuance of sustainable bonds is expected to reach USD 1 trillion by 2025, driven by lower interest rates and increased demand for financing green projects. These bonds are used to fund initiatives that have positive environmental and social impacts, such as clean energy projects, sustainable agriculture, and affordable housing.
- Biodiversity Finance: Investments aimed at preserving biodiversity are gaining traction. This includes funding for conservation projects, sustainable agriculture, and nature-based solutions. Biodiversity finance is becoming a critical component of sustainable investing as investors recognize the importance of protecting ecosystems.
- AI and ESG Integration: Artificial intelligence is being rapidly adopted to enhance ESG data analysis, helping investors make more informed decisions and manage risks effectively. AI can process vast amounts of data to identify ESG risks and opportunities, providing investors with valuable insights.
Impacts from the Trump Government
During President Trump’s administration, several policies significantly impacted sustainable investing:
- Climate Policy Changes: Trump’s withdrawal from the Paris Agreement and rollback of over 100 environmental regulations shifted focus away from renewable energy and ESG investments. Despite these federal policy changes, private capital continued to drive global climate funding, with renewable energy investments remaining economically viable.
- Deregulation and Traditional Energy Support: The Trump administration’s support for fossil fuel industries and deregulation efforts attracted investments back into carbon-based sectors like coal, oil, and natural gas. This shift posed challenges for ESG-focused funds, although consumer and investor demand for sustainability remained resilient.
- Impact on Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs): Trump’s stance on international agreements raised concerns about the performance of MDB bonds, which rely heavily on US support. However, MDB bonds continued to offer appealing yields and strong fundamentals, mitigating some of the impacts of reduced US government backing.
EU Responses
The European Union has taken proactive steps to support sustainable investing:
- Platform on Sustainable Finance: The EU’s Platform on Sustainable Finance monitors capital flows to sustainable investments, leveraging EU taxonomy data to guide policymaking and support a clean and competitive transition. This framework helps track the progress of large European corporates in aligning their capital expenditures with sustainability goals.
- Savings and Investment Union (SIU): The European Commission’s proposal for a European Savings and Investments Union aims to mobilize private savings to support sustainable finance. This initiative includes measures to enhance financial literacy, scale impact investment products, and unlock pension fund capital for sustainable projects.
- Omnibus Package: The EU’s Omnibus reforms reinforce Europe’s attractiveness as a hub for sustainable investment and industrial innovation. These regulatory changes contrast with the deregulatory tendencies observed in other major economies, particularly the United States.
Market Analysis
The sustainable investment market is experiencing significant growth:
- Global Market Size: The sustainable investment market was valued at approximately USD 6.718 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 42.935 billion by 2033, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 22.9%. This rapid growth reflects the increasing demand for investments that align with ESG principles.
- Assets Under Management (AUM): Sustainable equity and fixed-income funds reached a record 7.9% of global total AUM in the first half of 2023. This indicates a strong investor preference for sustainable investment options.
- US Market: In the United States, sustainable investments account for $52.5 trillion in assets under management, with $6.5 trillion explicitly marketed as ESG or sustainability-focused investments. This highlights the significant role of the US market in driving the growth of sustainable investing.
Examples of Sustainable Investments
- ESG-Focused Mutual Funds: These funds invest in companies that meet specific environmental, social, and governance criteria. For example, the Vanguard ESG U.S. Stock ETF allows investors to diversify their portfolios while adhering to ethical standards. These funds are designed to provide competitive returns while promoting sustainable business practices.
- Green Bonds: Green bonds are used to finance projects that have positive environmental impacts. These can include renewable energy installations, energy efficiency improvements, and sustainable water management. Green bonds offer investors a way to support environmental initiatives while earning returns.
- Thematic ETFs: Thematic ETFs focus on specific sustainability themes, such as clean energy, water conservation, or social justice. These funds allow investors to target their investments towards areas they are passionate about. For example, the iShares Global Clean Energy ETF invests in companies that produce energy from renewable sources.
- Eco-Friendly Real Estate: Investing in eco-friendly real estate involves funding properties that incorporate sustainable building practices, energy-efficient systems, and green certifications. These investments not only reduce environmental impact but also offer long-term financial benefits through energy savings and increased property values.
- Social Impact Bonds: These bonds fund projects that aim to achieve positive social outcomes, such as improving education, healthcare, or community development. Social impact bonds provide a way for investors to support initiatives that address critical social issues.
Sustainable investing is rapidly evolving, with new trends and opportunities emerging to address global challenges. The market is poised for substantial growth, driven by increased investor demand, regulatory support, and technological advancements. By investing in sustainable assets, investors can achieve financial returns while contributing to a more sustainable and equitable world.
#SustainableInvesting #ESG #ClimateAction #GreenBonds #BiodiversityFinance #AI #EcoFriendly #SocialImpact #MarketAnalysis #InvestmentTrends
-
The Growing Market for Recycled Clothing
Introduction
The fashion industry is undergoing a significant transformation as consumers and businesses alike increasingly prioritize sustainability. One of the most promising trends in this shift is the growing market for recycled clothing. This movement not only addresses environmental concerns but also offers economic benefits and innovative opportunities for companies like Loopi.
The global clothing recycling market is experiencing robust growth. In 2023, the market was valued at approximately USD 6.49 billion and is projected to reach USD 18.27 billion by 2033, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.9%. This growth is driven by rising awareness about the circular economy and the environmental impact of textile waste.
Sustainable fashion, which includes recycled clothing, is gaining traction. The market share of sustainable apparel is expected to reach over 6% by 2026. This trend is supported by increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly products and the adoption of sustainable practices by major fashion brands.
Environmental Impact
One of the significant benefits of recycled clothing is the reduction in microplastics released into the environment. Microplastics, tiny plastic particles less than 5mm in size, are a major pollutant originating from synthetic fibres used in clothing. These particles are released during the manufacturing, washing, and disposal of garments, eventually making their way into waterways and ecosystems.
Microplastics Statistics:
- Global Release: Approximately 5.6 million tonnes of synthetic microfibers have been released from apparel washing between 1950 and 2016, with half of this amount emitted in the last 10 years
- Laundry Impact: Up to 18 million microfibers may be released from a 13lb load of synthetic fabric laundry
- Cigarette Butts: Global cigarette butt pollution releases roughly 300,000 tons of microfibers into the environment annually
Recycled clothing helps mitigate this issue by reducing the demand for virgin synthetic fibers. Studies have shown that recycled polyester, for example, releases fewer microplastics compared to virgin polyester. This reduction in microplastic pollution is crucial for protecting marine life and maintaining the health of our ecosystems.
Companies Leading the Way
Loopi is a notable example of a company making strides in the recycled clothing market. Founded in 2019, Loopi (https://loopi.com) operates a second-hand apparel marketplace that offers a wide range of clothing items, enabling customers to make sustainable fashion choices while contributing to environmental conservation
Organizations like Cleaner Seas (https://www.cleaner-seas.com/) play a crucial role in addressing marine pollution and promoting sustainable practices. Established in 1998, Cleaner Seas focuses on a wide range of marine environmental issues, including the reduction of plastic pollution and the promotion of renewable energy in ocean conservation. Their efforts help raise awareness and drive action towards cleaner oceans, complementing the goals of the recycled clothing market.
Future Outlook
The future of the recycled clothing market looks promising, with several key trends driving its growth:
- Increased Consumer Awareness: As consumers become more aware of the environmental impact of their choices, the demand for recycled clothing is expected to rise.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in recycling technologies are making it easier and more cost-effective to produce high-quality recycled textiles.
- Regulatory Support: Governments and organizations are increasingly implementing policies and incentives to promote sustainable fashion practices.
The growing market for recycled clothing represents a significant shift towards sustainability in the fashion industry. Companies like Loopi and Cleaner Seas are leading the way by offering eco-friendly alternatives that reduce environmental impact and promote circular economy principles. With continued consumer support, technological advancements, and regulatory backing, the future of recycled clothing looks bright, promising a cleaner and more sustainable world.
-
The impacts of geopolitical change on ESG and BNG in the UK and on investor confidence.
Introduction
Geopolitical changes, such as the US’s shifting focus on international policies, have significant implications for Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) practices and Biodiversity Net Gain (BNG) initiatives in the UK. These changes can influence regulatory frameworks, investment flows, and corporate strategies, shaping the future of sustainability efforts in the UK.
Geopolitical Shifts and ESG
The US has seen a growing political divide over ESG practices, with some factions pushing back against what they term “woke capitalism.” This resistance is often driven by entrenched fossil fuel interests and industries fearing disruption
As the US re-focuses its geopolitical strategies, this anti-ESG sentiment could impact global capital markets and influence international regulatory standards. In contrast, the European Union (EU) continues to advance stringent sustainability regulations, maintaining momentum towards net-zero goals.
The UK’s alignment with EU standards, despite Brexit, suggests that it will continue to prioritize robust ESG frameworks. However, the UK’s approach may need to adapt to the evolving geopolitical landscape, balancing between US and EU influences.
Impacts on Biodiversity Net Gain (BNG)
BNG, a statutory requirement in the UK since 2024, mandates that new developments achieve at least a 10% net gain in biodiversity. This initiative aims to leave the natural environment in a better state post-development. The geopolitical climate can affect BNG in several ways:
- Investment and Funding:
- Geopolitical stability influences investor confidence. A stable geopolitical environment encourages investments in sustainable projects, including BNG initiatives. Conversely, geopolitical tensions can lead to market volatility, affecting funding for biodiversity projects2.
- Regulatory Alignment:
- The UK’s BNG policies are influenced by broader international environmental agreements and standards. Changes in US policies could lead to shifts in global environmental priorities, potentially impacting the UK’s regulatory approach to BNG.
- Corporate Strategies:
- Companies operating in the UK may need to navigate differing ESG expectations from US and EU markets. This could lead to a more complex compliance landscape, requiring businesses to adopt flexible and adaptive strategies to meet varied regulatory requirements.
Examples of Geopolitical Changes Impacting ESG
- US Withdrawal from Climate Agreements:
- The US’s withdrawal from the Paris Agreement under the Trump administration in 2017 and again in 2025 has had significant repercussions2. This move undermined global climate cooperation, potentially encouraging other nations to delay or reduce their own commitments. It also created uncertainty in global markets, affecting investment in green technologies and sustainability initiatives.
- Executive Orders on Energy Policy:
- Recent executive orders in the US, such as those declaring a national energy emergency and prioritizing fossil fuel production, have rolled back renewable energy incentives and suspended key environmental regulations1. These actions can weaken global efforts to combat climate change and shift focus away from sustainable practices.
- Impact on Global Climate Finance:
- The US is a key contributor to the $100 billion global climate fund pledged to support developing nations. Withdrawal from climate agreements and reduced federal contributions can limit funding for climate resilience projects worldwide2.
Impact on Investor Confidence
Geopolitical changes significantly impact investor confidence in ESG and BNG businesses:
- Market Volatility:
- Geopolitical tensions disrupt supply chains and heighten market volatility, complicating corporate sustainability efforts1. Investors may become cautious, reducing their willingness to fund ESG and BNG initiatives due to perceived risks.
- Financing Constraints:
- Increased geopolitical risks can lead to financing constraints for ESG-focused businesses2. Investors may demand higher returns to compensate for the perceived risks, making it more challenging for companies to secure funding for sustainability projects.
- Government Subsidies and Support:
- Government subsidies and support can mitigate the negative effects of geopolitical risks on ESG performance2. Increased investor attention and government incentives can help alleviate financing constraints, encouraging investment in ESG and BNG initiatives.
Future Outlook
The future of ESG and BNG in the UK will likely be shaped by several key factors:
- Continued Regulatory Development:
- The UK is expected to continue strengthening its ESG and BNG regulations, aligning with EU standards while considering global geopolitical dynamics. This will involve refining metrics for measuring biodiversity gains and enhancing enforcement mechanisms.
- Increased Private Sector Engagement:
- As awareness of environmental issues grows, more businesses are likely to integrate ESG and BNG into their core strategies. This trend will be driven by both regulatory requirements and market demand for sustainable practices.
- Technological Advancements:
- Innovations in technology, such as AI and automation, will play a crucial role in advancing ESG and BNG initiatives. These technologies can improve data collection, monitoring, and reporting, making it easier for companies to comply with regulations and achieve sustainability goals.
- Global Collaboration:
- The UK will need to engage in international collaborations to address global environmental challenges. This includes participating in international agreements and working with other nations to promote sustainable development.
Conclusion
Geopolitical changes, particularly those stemming from the US’s shifting focus, have significant implications for ESG and BNG in the UK. While these changes present challenges, they also offer opportunities for the UK to strengthen its commitment to sustainability. By continuing to develop robust regulatory frameworks, engaging the private sector, leveraging technological advancements, and fostering global collaboration, the UK can navigate the complexities of the geopolitical landscape and lead the way in sustainable development.
- Investment and Funding:
-
The State of IT Managed Service Providers in the UK
The IT managed service provider (MSP) sector in the UK is a robust and dynamic industry, playing a crucial role in the nation’s digital economy. As of 2022, the UK MSP market comprised approximately 11,492 active providers, generating annual revenues of £52.6 billion. This sector supports around 294,340 full-time employees, contributing significantly to the UK’s economic health
The MSP landscape is diverse, with large providers accounting for just 4% of firms but generating 74% of total revenue. Medium-sized MSPs make up 9% of firms and contribute 16% of revenue, while small and micro MSPs, which constitute the majority, generate the remaining 10%. This distribution highlights the concentration of market power among the largest providers yet underscores the vital role of smaller MSPs in driving innovation and catering to niche markets.
The future of the UK MSP market looks promising, with substantial growth anticipated over the next decade. The market is expected to grow from USD 15.35 billion in 2023 to USD 28.29 billion by 2032, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.03%. Several factors are driving this growth:
- Digital Transformation: Businesses are increasingly outsourcing IT management to focus on core operations, ensuring scalability, security, and efficiency
- Cybersecurity: The rise in cybersecurity threats is fuelling demand for managed security services, as companies seek expert assistance to protect sensitive data and systems
- Cloud Computing: Adoption of cloud computing and advanced technologies like artificial intelligence and automation are contributing to market expansion
- Remote Work: The shift towards remote and hybrid work models accelerates the need for managed services that offer seamless support, robust network management, and collaboration tools
Several key growth markets are emerging within the UK MSP sector:
- Managed Security Services: As cybersecurity threats continue to evolve, managed security services are becoming increasingly vital. This segment is expected to register the fastest growth during the forecast period
- Cloud Services: The demand for cloud-based solutions, including desktop-as-a-service and virtual desktop infrastructure, is rising due to their flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and scalability
- Managed Workplace Services: With the growing adoption of hybrid work environments, managed workplace services that enhance end-user experiences and ensure smooth IT support for remote workers are in high demand
- AI and Automation: Innovations in artificial intelligence and automation are transforming the MSP landscape, offering new opportunities for efficiency and service delivery
Key Challenges
Despite the promising outlook, MSPs in the UK face several significant challenges:
- Cybersecurity Threats: The increasing frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks pose a major challenge. MSPs must continuously invest in advanced security measures to protect their own infrastructure and that of their clients
- Compliance and Regulations: Adhering to stringent regulations such as GDPR and other data protection laws is crucial. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines and damage to reputation
- Revenue Pressures: The competitive landscape puts pressure on MSPs to maintain profitability while offering high-quality services. Smaller MSPs, in particular, may struggle with pricing strategies and cost management
- Talent Shortage: The shortage of skilled IT professionals makes it difficult for MSPs to recruit and retain talent. This challenge is exacerbated by the growing demand for specialized skills in cybersecurity and cloud computing
- Technological Advancements: Keeping up with rapid technological changes requires continuous investment in training and infrastructure. MSPs must stay ahead of the curve to remain competitive
The UK MSP sector is poised for significant growth, driven by digital transformation, cybersecurity needs, cloud adoption, and the shift to remote work. However, MSPs must navigate challenges such as cybersecurity threats, regulatory compliance, revenue pressures, talent shortages, and rapid technological advancements. By addressing these challenges and capitalizing on key growth markets, MSPs can continue to play a critical role in supporting the UK’s digital economy.
-
The Importance of Biodiversity Net Gain (BNG) in New Developments
At Kognise, we believe that businesses have a significant responsibility to ensure their new developments positively contribute to the environment. Biodiversity Net Gain (BNG) is a crucial aspect of this responsibility, now mandated by law, which requires projects to leave the natural environment in a measurably better state than before. This entails achieving a minimum of 10% net gain in biodiversity compared to the pre-development baseline.
Understanding BNG Responsibilities
- Pre-Planning:
- Conduct a comprehensive BNG assessment with an ecologist to determine the required BNG units.
- Planning:
- Submit a draft Biodiversity Gain Plan (BGP) alongside the planning application. This should include a Supply and Assurance Agreement.
- Post-Planning:
- Complete the purchase of BNG units and submit the final BGP to the Local Planning Authority (LPA) to fulfill the condition.
Legislation Enforcing BNG
The enforcement of BNG is governed under Schedule 7A of the Town and Country Planning Act 1990, as introduced by Schedule 14 of the Environment Act 2021. This statutory framework stipulates that developments must deliver at least a 10% increase in biodiversity value relative to the pre-development biodiversity value of the onsite habitat.
Long-Term Commitment
Once a development achieves its BNG commitments, the responsibility does not end there. The biodiversity of the site must be maintained for at least 30 years, ensuring that these gains are preserved for future generations. This obligation is legally tied to the land, making it a long-term commitment that businesses must uphold.
Embracing Sustainability
By incorporating BNG into our projects, we not only comply with legal requirements but also make a significant contribution to a sustainable future. Embracing BNG provides an excellent opportunity to positively impact our environment, ensuring that our developments are beneficial to both business and nature.
At Kognise, we are committed to supporting businesses in integrating BNG into their projects, offering expertise and guidance to navigate these requirements successfully. Together, we can build a sustainable future that prioritizes the health and well-being of our natural environment.
For more information BNG implementation, feel free to contact us today.
#BiodiversityNetGain #SustainableDevelopment #EnvironmentalResponsibility #BNG #GreenBuilding #EcoFriendly #Sustainability #FutureProof #NatureConservation #BusinessResponsibility
- Pre-Planning:
-
Funding Options for Startups & Small Businesses: Where to Find the Cash to Grow
For startups and small businesses, securing funding is often the biggest hurdle to growth. Whether you’re launching a new venture, expanding operations, or investing in innovation, having access to the right financial support can make all the difference.
But where do these funds come from, and how can businesses access them? Here’s a breakdown of the key funding options available and how investment advisory firms like Kognise help businesses navigate the process.
1. Bootstrapping: Funding Growth from Within
Many entrepreneurs self-fund their businesses, using personal savings, reinvesting profits, or tapping into early revenue streams.
✅ Pros: Full control over the business, no interest or equity dilution.
❌ Cons: High financial risk, limited scalability.💡 How to Access: Start by minimizing costs, reinvesting revenue, and keeping overheads low in the early stages.
2. Friends, Family & Angel Investors
Startups often turn to personal networks or individual investors (angels) who provide capital in exchange for equity.
✅ Pros: Flexible terms, potential mentorship from angel investors.
❌ Cons: Mixing business with personal relationships can be risky, and angel investors may seek significant equity.💡 How to Access: Platforms like the UK Business Angels Association (UKBAA) or Angel Investment Network help connect businesses with angel investors.
3. Government Grants & Loans
Governments and local authorities offer grants, loans, and tax relief schemes to support small businesses and startups.
✅ Pros: Non-repayable grants or low-interest loans, no equity loss.
❌ Cons: Competitive application process, strict eligibility criteria.💡 How to Access:
- Innovate UK Grants – Funding for research and innovation projects.
- Start Up Loans (British Business Bank) – Loans of up to £25,000 with mentoring support.
- R&D Tax Credits – Helps businesses reclaim tax on innovation-related costs.
4. Venture Capital (VC) Funding
For high-growth startups, venture capitalists (VCs) provide investment in exchange for equity, usually in multiple funding rounds.
✅ Pros: Large sums of funding, access to industry expertise.
❌ Cons: Loss of equity, pressure for rapid growth and returns.💡 How to Access:
- Research VCs specializing in your sector (e.g., Seedcamp, Balderton Capital).
- Prepare a strong pitch deck and demonstrate market potential.
- Seek introductions via industry events and networking platforms.
5. Crowdfunding: Raising Capital from the Public
Crowdfunding allows businesses to raise money from a large number of small investors via platforms like Crowdcube, Seedrs, or Kickstarter.
✅ Pros: Can build brand awareness, doesn’t always require giving up equity.
❌ Cons: Requires strong marketing, risk of failure to meet funding targets.💡 How to Access:
- Choose between equity crowdfunding (selling shares) or reward-based crowdfunding (offering products or perks).
- Create a compelling campaign and promote it across social media.
6. Business Loans & Alternative Lenders
Traditional bank loans and alternative lenders provide funding for businesses with a solid financial history.
✅ Pros: Retain full ownership, structured repayment plans.
❌ Cons: Requires good credit history, potential high interest rates.💡 How to Access:
- High street banks (e.g., Barclays, HSBC, NatWest) offer SME loans.
- Alternative lenders like Funding Circle provide faster, flexible financing options.
7. Corporate Investment & Strategic Partnerships
Larger companies sometimes invest in or partner with startups that align with their business strategy.
✅ Pros: Access to funding, resources, and industry expertise.
❌ Cons: Risk of losing independence, reliance on corporate priorities.💡 How to Access:
- Approach corporations with aligned interests.
- Pitch your business as a strategic investment opportunity.
8. Investment Advisory Firms: The Role of Kognise
Navigating funding options can be complex, and that’s where investment advisory firms like Kognise come in.
🔹 Investor Matching – Identifying the right funding sources for your business.
🔹 Pitch Deck & Business Plan Support – Refining investment proposals for maximum impact.
🔹 Due Diligence Preparation – Ensuring financials and business models meet investor standards.
🔹 Deal Structuring & Negotiation – Securing the best terms for funding agreements.Having the right guidance increases your chances of securing investment while ensuring sustainable growth.
Final Thoughts: Choosing the Right Funding Strategy
The best funding option depends on your business stage, growth plans, and risk tolerance. Many businesses use a combination of funding sources to maximize opportunities while minimizing risks.
🔹 Early-stage? Start with bootstrapping, grants, and angel investors.
🔹 Scaling up? Consider venture capital, business loans, or crowdfunding.
🔹 Looking for strategic growth? Corporate investment or advisory-led funding may be the best route.No matter which path you take, preparation is key—so get your business plan, financials, and pitch ready to impress potential investors.
-
How AI Accelerates Business Growth and Reduces Costs
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the business landscape by offering innovative solutions that enhance efficiency, automate processes, and drive significant cost savings. From small startups to large enterprises, AI-powered tools are transforming how businesses operate, compete, and grow.
1. AI in Process Automation
One of the most immediate and impactful uses of AI is process automation. Businesses can leverage AI-powered Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to handle repetitive and rule-based tasks that previously required human effort. Examples include:
- Invoice Processing – AI-driven automation tools can extract, verify, and process invoice data, reducing errors and time spent on manual entry.
- Customer Onboarding – AI automates identity verification, document processing, and account creation, improving customer experience and reducing onboarding time.
- HR and Payroll – AI simplifies recruitment by screening resumes and automating payroll processing, saving significant labour costs.
By automating these processes, businesses can free up human employees for higher-value tasks, increasing productivity and efficiency.
2. AI in Customer Support and Service
AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants are reshaping customer service by offering 24/7 support, reducing wait times, and lowering customer service costs. AI-powered tools such as:
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants – These can handle common customer queries, troubleshoot issues, and escalate complex cases to human agents when needed.
- AI-powered Call Centres – AI tools analyse speech and text to offer real-time responses, assisting agents with accurate information and reducing resolution times.
- Sentiment Analysis – AI can analyse customer feedback and online reviews to detect sentiments and improve service quality proactively.
By leveraging AI in customer service, businesses can enhance customer satisfaction while reducing labor costs and response times.
3. AI in Sales and Marketing
AI is revolutionizing sales and marketing by optimizing campaigns, predicting customer behavior, and automating lead generation. Some key applications include:
- Predictive Analytics – AI analyses historical customer data to predict future buying behaviour, enabling businesses to target the right audience with personalized offers.
- Automated Content Generation – AI-driven tools like GPT-powered chatbots can generate blog posts, social media updates, and email marketing campaigns, saving time and resources.
- Ad Optimization – AI platforms like Google Ads and Facebook Ads leverage machine learning to optimize ad placements and improve conversion rates.
- Dynamic Pricing – AI analyses market trends and competitor pricing to adjust product prices dynamically for maximum profitability.
With AI-powered marketing, businesses can reduce advertising costs while improving campaign effectiveness and customer engagement.
4. AI in Data Analytics and Decision-Making
AI-powered data analytics tools enable businesses to make data-driven decisions faster and more accurately. Key applications include:
- Business Intelligence – AI-powered tools analyse vast amounts of data to identify trends, generate insights, and suggest data-backed decisions.
- Risk Management – AI assesses potential risks in investments, fraud detection, and cybersecurity threats, helping businesses mitigate financial losses.
- Supply Chain Optimization – AI predicts demand, manages inventory, and optimizes logistics to reduce costs and prevent overstocking or understocking.
AI-driven analytics help businesses improve efficiency, reduce waste, and optimize resource allocation.
5. AI in Human Resources and Talent Acquisition
Recruitment and talent management can be costly and time-consuming, but AI streamlines these processes through:
- AI-Powered Resume Screening – AI tools analyse and rank resumes based on job descriptions, reducing hiring time.
- Employee Performance Monitoring – AI-driven tools track employee productivity, engagement, and well-being, helping HR teams make data-driven decisions.
- Training and Development – AI-powered learning platforms personalize training programs, enhancing employee skills while reducing training costs.
By leveraging AI in HR, businesses can enhance talent acquisition and workforce management while reducing administrative costs.
6. AI in Financial Management
AI is transforming financial management by automating accounting, fraud detection, and investment analysis. Key applications include:
- Automated Bookkeeping – AI tools like Xero and QuickBooks automate financial transactions, reducing errors and accounting costs.
- Fraud Detection – AI analyses transaction patterns to identify fraudulent activities and prevent financial losses.
- Investment and Forecasting – AI-powered financial models analyse market trends and predict investment opportunities, optimizing business growth strategies.
AI in financial management enhances accuracy, prevents fraud, and ensures better financial planning.
7. AI in Manufacturing and Operations
Manufacturing businesses are benefiting from AI-powered automation and predictive maintenance. Key applications include:
- Smart Manufacturing – AI-powered robotics automate assembly lines, reducing production costs and improving efficiency.
- Predictive Maintenance – AI predicts machine failures before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Quality Control – AI-powered visual inspection detects defects in products, improving quality assurance.
AI-driven manufacturing solutions enhance productivity, reduce waste, and optimize operational costs.
8. AI in Cybersecurity and IT Management
AI strengthens cybersecurity by identifying and preventing cyber threats in real-time. Key applications include:
- Threat Detection – AI identifies unusual network activities and detects potential cyber-attacks before they escalate.
- Automated Security Patching – AI systems automatically update and patch security vulnerabilities, reducing IT maintenance costs.
- Fraud Prevention – AI monitors transactions and detects fraudulent activities, minimizing financial losses.
By implementing AI-driven cybersecurity solutions, businesses can reduce security risks and avoid costly data breaches.
Conclusion
AI is no longer a futuristic concept but a critical tool for businesses looking to scale efficiently while cutting costs. By integrating AI into various aspects of operations, businesses can automate processes, enhance decision-making, improve customer experiences, and optimize financial management.
From AI-powered automation to intelligent analytics, the potential for AI in business growth is limitless. As technology advances, businesses that embrace AI will stay ahead of the competition, reduce operational costs, and accelerate growth in an increasingly digital world. Investing in AI today is not just an option but a necessity for future success.
-
The Hottest Seed Fund Markets in 2025
In 2025, the startup ecosystem is witnessing significant shifts in seed funding trends, with certain sectors and regions emerging as hotspots for early-stage investments. Investors are keenly focusing on industries that promise innovation and substantial growth potential.
Key Sectors Attracting Seed Funding:
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI continues to be a magnet for seed investments, with applications spanning various industries. Startups leveraging AI to enhance business processes, customer experiences, and data analytics are particularly appealing to investors. For instance, companies like Perplexity AI have developed AI-powered conversational search engines, attracting significant funding.
Fintech: The financial technology sector remains robust, with a surge in AI-powered fintech startups. These companies are innovating in areas such as automated banking, investment management, and financial compliance. Notable examples include startups like BeatBread, which provides financial advances to artists based on AI-analyzed revenue potential.
Health and Longevity: There’s a growing interest in startups focusing on health, wellness, and longevity. Investors are funding companies that bridge science and wellness, aiming to scale innovations in medical technology, nutrition, and wellness solutions. Clinique La Prairie’s Longevity Fund, for example, has launched a €100 million investment fund aimed at scaling companies that bridge science and longevity.
Climate Tech: Environmental sustainability is a pressing global concern, leading to increased investments in climate tech startups. Companies developing solutions for carbon capture, renewable energy, and sustainable agriculture are gaining traction. For instance, Paebbl is mitigating CO2 emissions by turning CO2 into solid carbonate materials using rock weathering.
Regional Hotspots:
Silicon Valley: Maintaining its dominance, Silicon Valley secured $90 billion in venture capital investment in 2024, accounting for 57% of global venture funding. This is attributed to the region’s strong AI presence, access to Big Tech, and established startup infrastructure.
Helsinki, Finland: Helsinki’s startup scene is thriving, particularly around Aalto University and the Slush festival. The city fosters innovation with supportive entrepreneurs, investors, and a collaborative mentality. Emerging startups in Helsinki include Distance Technologies, developing mixed-reality HUDs for various applications, and Steady Energy, working on low-temperature nuclear reactors for district heating.
2025 presents a dynamic landscape for seed funding, with investors gravitating towards sectors that offer innovative solutions and substantial growth potential. Startups operating in AI, fintech, health, and climate tech, particularly in vibrant ecosystems like Silicon Valley and Helsinki, are well-positioned to attract early-stage investments
-
The Impact of Geopolitical Changes on Habitat Banks and ESG
Recent geopolitical shifts are reshaping the environmental, social, and governance (ESG) landscape, directly affecting habitat banks and nature-based solutions. Governments, corporations, and investors must adapt to these changes to maintain regulatory compliance and achieve sustainable growth.
Geopolitical Tensions and ESG Regulations
Ongoing geopolitical conflicts and shifting alliances have altered environmental policies globally. For instance, the European Union’s Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD) requires companies to account for environmental and social risks across their supply chains. Meanwhile, China’s tightening ESG reporting regulations reflect a growing focus on sustainability despite geopolitical competition with Western economies. These regulatory pressures impact businesses engaged in habitat banking, which relies on stable policies and market incentives to function effectively.
The Rise of Nationalism and Its Effects on Habitat Banking
Many countries are prioritizing national interests over multilateral environmental agreements. For example, the United States’ Inflation Reduction Act incentivizes domestic clean energy production but does not include international biodiversity funding. This shift means that habitat banks, which rely on cross-border conservation financing, may struggle to secure international investments.
Additionally, in the UK, post-Brexit regulatory independence has led to changes in biodiversity net gain (BNG) policies. While the UK government mandates BNG for new developments, funding gaps and policy uncertainty could slow the growth of habitat banks. Businesses investing in habitat creation need to navigate these changes to align with national conservation strategies.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Biodiversity Credits
Geopolitical instability has also affected global supply chains, impacting industries reliant on biodiversity credits. The war in Ukraine, for instance, has disrupted agricultural exports, leading to increased land use pressures in alternative markets like Brazil and Indonesia. This intensifies deforestation risks, complicating efforts to establish habitat banks in these regions.
As a response, corporations are integrating ESG risk assessments into their supply chains. Companies such as Unilever and Nestlé are leveraging satellite monitoring and AI-driven analytics to ensure biodiversity commitments remain intact despite supply chain challenges. By doing so, they protect their ESG credentials while supporting habitat banking initiatives.
Opportunities for Strategic Adaptation
While geopolitical uncertainty presents challenges, it also opens new opportunities. Governments and businesses can foster resilience in habitat banking by:
- Aligning with Emerging Standards: Companies should proactively comply with evolving ESG regulations, such as the EU’s Nature Restoration Law, to ensure long-term viability.
- Investing in Nature-Based Solutions: Organizations can enhance biodiversity commitments by supporting domestic habitat banks, reducing reliance on international programs affected by geopolitical shifts.
- Leveraging Public-Private Partnerships: Collaborating with governments and NGOs can secure funding for habitat conservation amid uncertain policy landscapes.
Conclusion
Geopolitical changes will continue to shape the future of ESG and habitat banking. Organizations that remain agile, anticipate policy shifts, and integrate robust ESG strategies will be better positioned to navigate these complexities. By proactively addressing risks and capitalising on emerging opportunities, businesses can drive meaningful environmental and social impact despite geopolitical challenges.
-
ESG Projects and Investments in 2025: Navigating Opportunities and Challenges
The year 2025 marks a pivotal point for Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) projects and investments. As the world grapples with climate change, social equity, and corporate accountability, ESG-focused initiatives continue to shape the global economic landscape. However, the return of Donald Trump to the U.S. presidency in 2025 introduces complexities that may influence the trajectory of ESG investments.
1. The Growth of ESG Investments
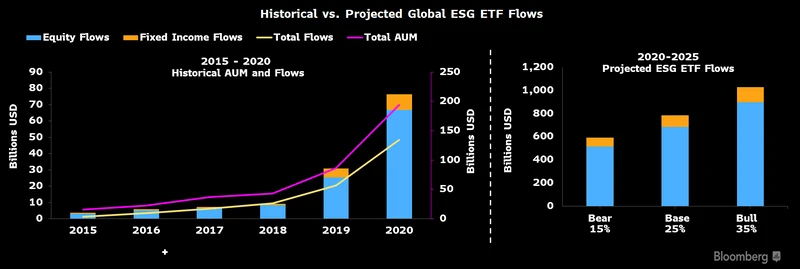
Despite economic uncertainties, ESG investments remain robust. According to Bloomberg, global ESG assets under management (AUM) are expected to reach $50 trillion by the end of 2025, accounting for over one-third of total global AUM. This growth is driven by increasing investor demand for sustainable assets, the rise of green bonds, and corporate commitments to achieving net-zero emissions.
For instance, renewable energy projects continue to dominate ESG portfolios. The International Energy Agency (IEA) reports that investments in solar and wind energy surged by 12% in 2024, reflecting a strong commitment to reducing global carbon emissions. Companies like Tesla and Orsted have expanded their renewable energy initiatives, contributing to the decarbonization of key industries.
2. The Impact of Trump’s Presidency on ESG Policies
Donald Trump’s presidency in 2025 introduces potential headwinds for ESG investments, particularly in the United States. Historically, Trump’s policies favored deregulation and traditional energy sectors, including oil and gas. If similar policies are implemented, the growth of ESG initiatives in the U.S. may face significant challenges.
Environmental Impact: During Trump’s first term, the U.S. withdrew from the Paris Climate Accord and rolled back over 100 environmental regulations. A return to such policies in 2025 could reduce federal support for renewable energy projects and weaken global climate initiatives. For example, the Inflation Reduction Act, which allocated $369 billion to climate programs under the Biden administration, may face scaling back, impacting clean energy investments.
Social and Governance Challenges: Corporate governance and social equity initiatives may also encounter reduced emphasis. Policies promoting diversity, inclusion, and labor rights could face rollbacks, potentially influencing investor perceptions of U.S.-based ESG assets. According to PwC, 81% of global investors prioritize mandatory ESG disclosures; reduced regulatory enforcement may erode confidence in American corporations.
3. Regional and Sectoral Resilience
Despite potential U.S. policy shifts, other regions are expected to maintain their ESG momentum. The European Union (EU) remains a leader, with its Green Deal targeting carbon neutrality by 2050. Asia-Pacific markets are also emerging as strong players, with China and India increasing investments in renewable energy and sustainable infrastructure.
Sectors such as technology and healthcare are likely to thrive in ESG contexts. For example, Microsoft’s commitment to becoming carbon negative by 2030 continues to inspire global tech companies. Similarly, ESG-focused healthcare firms are addressing social challenges by expanding access to affordable treatments and vaccines.
4. Investor Strategies for 2025
Given the potential impact of Trump’s presidency, investors are likely to adopt diversified strategies to mitigate risks. These include:
- Geographical Diversification: Allocating funds to regions with stronger ESG commitments, such as the EU and Asia-Pacific.
- Thematic Investing: Focusing on high-growth areas like renewable energy, electric vehicles, and sustainable agriculture.
- Engagement: Collaborating with corporations to advocate for stronger ESG practices, even in challenging regulatory environments.
Conclusion
ESG projects and investments in 2025 remain a cornerstone of global sustainability efforts, with significant opportunities for growth and innovation. The return of Donald Trump to the U.S. presidency introduces uncertainties, particularly in environmental and social policy domains. Investors must navigate these challenges by adopting proactive strategies and leveraging opportunities in resilient markets and sectors. As the world transitions toward a more sustainable future, the balance between policy shifts and market-driven initiatives will shape the success of ESG efforts in the years to come.